Endocrine System
Adrenal Gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia, Subcapsular
Narrative
This change is characterized by increased numbers of adrenal cortical subcapsular cells, generally considered to be the multipotential stem/progenitor cells that replenish senescent cells in the inner cortical zones. Under appropriate hormonal stimulation, the subcapsular cells can transdifferentiate into sex-steroid–producing cells resembling stromal gonadal cells. Two morphologically different types of subcapsular cells may be present in subcapsular hyperplastic lesions: elongated, spindle or fusiform type A cells (Figure 5) with elliptical nuclei and scanty basophilic cytoplasm, and larger, round or polygonal type B cells (Figure 6) with more abundant, pale to clear cytoplasm and round nuclei. Early hyperplastic lesions (Figure 1 and Figure 2) consist of small, often linear foci composed primarily of the spindle-like type A cells. The cell clusters are located initially in the zona glomerulosa adjacent to the capsule (Figure 1 and Figure 2), but as the cell aggregates enlarge due to proliferation, they extend centripetally as narrow to broad wedges intercalated between the underlying zona fasciculata cell cords and in linear sheets parallel to the adrenal capsule (Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3). As the hyperplastic lesions enlarge, type B cells appear, and with further progression the ratio of polygonal type B cells to spindle type A cells usually increases (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Multiple foci in a given adrenal gland may coalesce to form an almost continuous band of hyperplastic cells subjacent to the capsule (Figure 7). Very large foci (Figure 8) are often composed almost entirely of polygonal type B cells, with few elongated type A cells, and can exhibit some degree of compression and expansion.
Focal subcapsular hyperplasia is considered a proliferative lesion in a morphologic continuum that can progress to adenoma and, rarely, to carcinoma. Subcapsular adenomas are also composed of variable mixtures of well-differentiated "spindle" and "polygonal" cells, so differentiating large focal hyperplasias from smaller adenomas can be challenging. Compared with hyperplastic foci, adenomas are larger, are more discretely nodular, clearly compress the adrenal parenchyma, and may even bulge prominently above the capsular surface due to pronounced expansile proliferation.
Bielinska M, Kiiveri S, Parviainen H, Mannisto S, Heikinheimo M, Wilson DB. 2006. Gonadectomy-induced adrenocortical neoplasia in the domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo) and laboratory mouse. Vet Pathol 43:97-117.
Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16537928Bielinska M, Porter-Tinge SB, Kiiveri S, Genova E, Rahman N, Huhtanemi IT, Muglia LJ, Heikinheimo M, Wilson DB. 2003. Mouse strain susceptibility to gonadectomy-induced adrenocortical tumor formation correlates with the expression of GATA-4 and luteinizing hormone receptor. Endocrinology 144:4123-4133.
Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12933687Brayton CF, Treuting PM, Ward JM. 2012. Pathobiology of aging mice and GEM: Background strains and experimental design. Vet Pathol 49:85-105.
Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22215684Dunn TB. 1970. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the adrenal gland of the mouse, including neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst 44:1323-1389.
Abstract: http://jnci.oxfordjournals.org/content/44/6/1323.abstractGoodman DG. 1983. Subcapsular cell hyperplasia, adrenal, mouse. In: Monographs on the Pathology of Laboratory Animals: Endocrine System (Jones TC, Mohr U, Hunt RD, eds). Springer, Berlin, 66-68.
Abstract: http://www.springer.com/medicine/pathology/book/978-3-642-64649-2Kim JS, Kubota H, Kiuchi Y, Doi K, Saegusa J. 1997. Subcapsular cell hyperplasia and mast cell infiltration in the adrenal cortex of mice: Comparative study in 7 inbred strains. Exp Anim 46:303-306.
Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9353639Krachulec J, Vetter M, Schrade A, Löbs AK, Bielinska M, Cochran R, Kyrönlahti A, Pihlajoki M, Parviainen H, Jay PY, Heikinheimo M, Wilson DB. 2012. GATA4 is a critical regulator of gonadectomy-induced adrenocortical tumorigenesis in mice. Endocrinology 153:2599-2611.
Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22461617National Toxicology Program. 2011. NTP TR-570. Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of α,β-Thujone (CAS No. 76231-76-0) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies). NTP, Research Triangle Park, NC.
Abstract: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/go/36137National Toxicology Program. 2013. NTP TR-578. Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Gingko biloba Extract in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies). NTP, Research Triangle Park, NC.
Abstract: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/go/37193Nyska A, Maronpot RR. 1990. Adrenal gland. In: Pathology of the Mouse: Reference and Atlas (Maronpot RR, Boorman GA, Gaul BW, eds). Cache River Press, Vienna, IL, 509-536.
Abstract: http://www.cacheriverpress.com/books/pathmouse.htmTaylor I. 2011. Mouse. In: Background Lesions in Laboratory Animals: A Color Atlas (McInnes EF, ed). Saunders Elsevier, Amsterdam, 45-72.
Abstract: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780702035197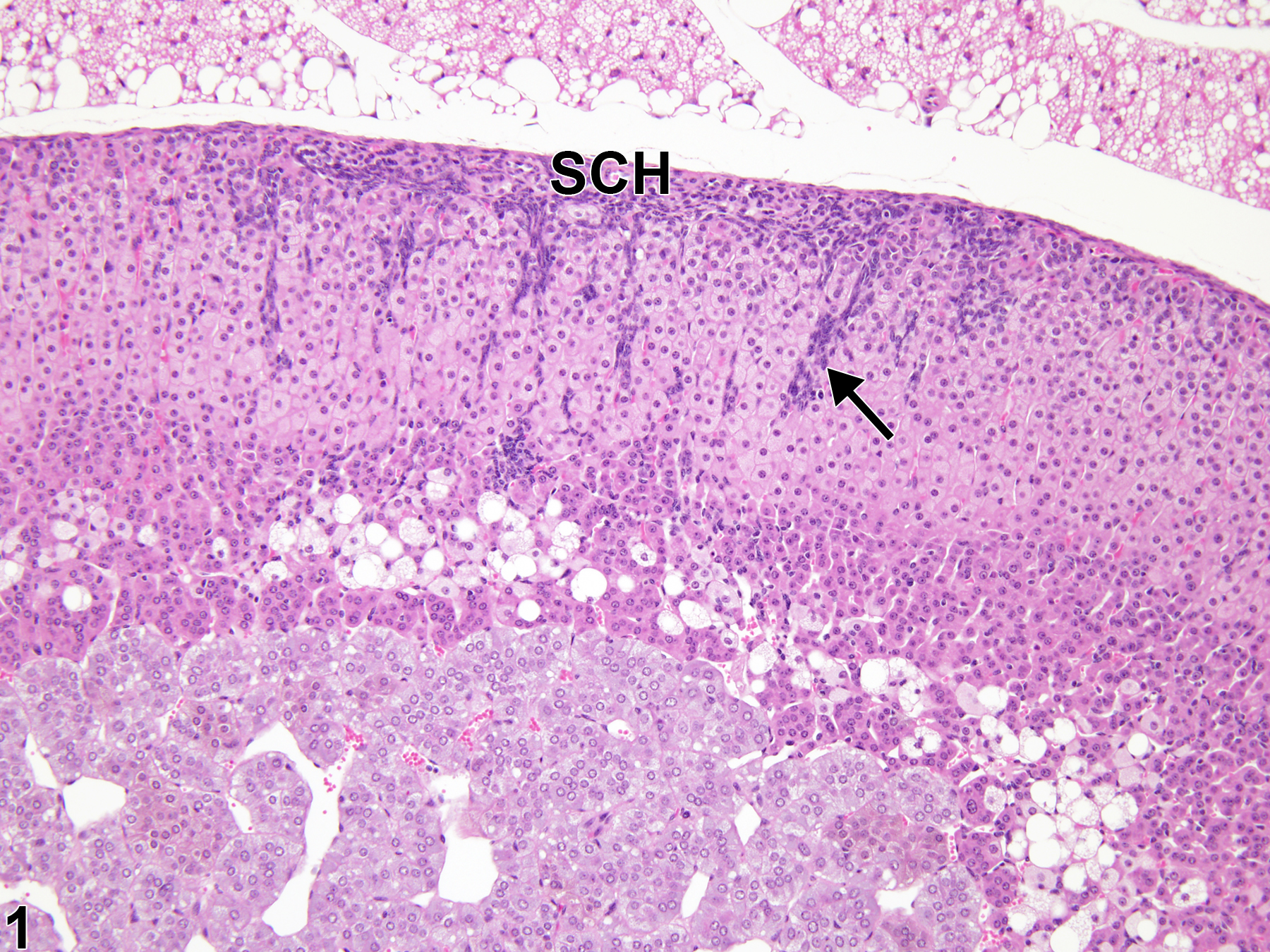
Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia, Subcapsular in a female Tg.AC (FVB/N) hemizygous mouse from a subchronic study. Early-stage subcapsular cell hyperplasia (SCH) is characterized by subcapsular foci of small, basophilic cells that extend into the zona fasciculata (arrow).
All Images

Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia, Subcapsular in a female Tg.AC (FVB/N) hemizygous mouse from a subchronic study (higher magnification of Figure 1). Early-stage subcapsular hyperplasia is composed primarily of smaller, more basophilic, fusiform, type A cells that extend into the zona fasciculate.

Adrenal gland, Cortex - Hyperplasia, Subcapsular in a female B6C3F1/N mouse from a chronic study (higher magnification of Figure 3). The subcapsular hyperplasia is characterized by proliferation of smaller, fusiform, basophilic type A (A) cells with nests of larger, paler, polygonal type B cells (B).







