Respiratory System
Lung, Alveolar/Bronchiolar Epithelium - Hyperplasia
Narrative
Boorman GA, Eustis SL. 1990. Lung. In: Pathology of the Fischer Rat: Reference and Atlas (Boorman GA, Eustis SL, Elwell MR, Montgomery CA, MacKenzie WF, eds). Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 339-367.
Dixon D, Herbert RA, Sills RC, Boorman GA. 1999. Lungs, pleura, and mediastinum. In: Pathology of the Mouse: Reference and Atlas (Maronpot RR, Boorman GA, Gaul BW, eds). Cache River Press, Vienna, IL, 293-332.
Renne, R, Brix A, Harkema J, Herbert R, Kittle B, Lewis D, March T, Nagano K, Pino M, Rittinghausen S, Rosenbruch M, Tellier P, Wohrmann T. 2009. Proliferative and nonproliferative lesions of the rat and mouse respiratory tract. Toxicol Pathol 37(suppl):5S-73S.
Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20032296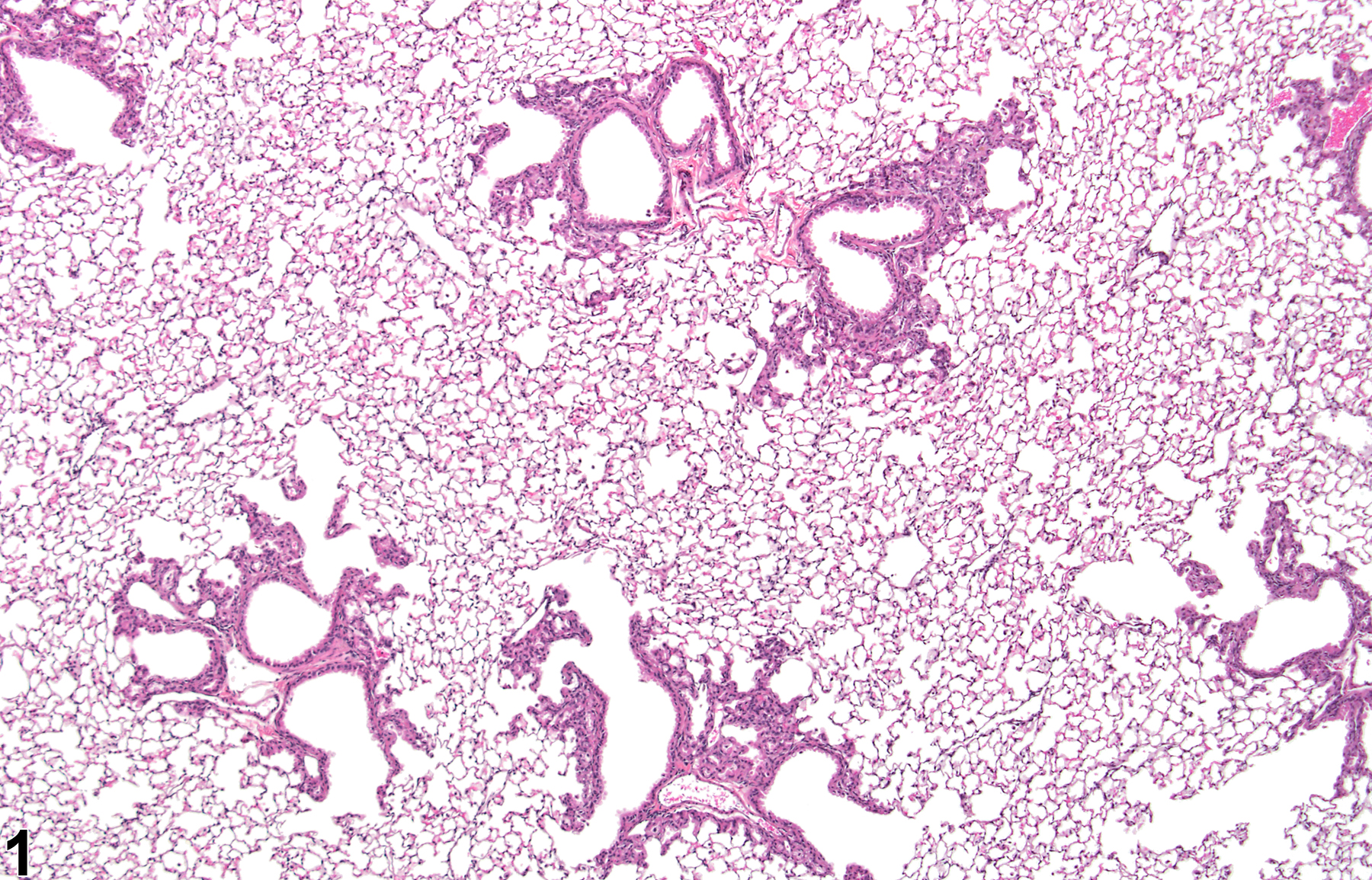
Lung, Alveolar/bronchiolar epithelium - Hyperplasia in a male B6C3F1/N mouse from a chronic study. This low-magnification image shows the distribution of the lesion.






