Musculoskeletal System
Bone - Cyst
Narrative
Cortical bone cysts (aneurysms) are characterized by expansion of the cortex and/or marrow cavity by an expansile cystic space composed of a thin wall of cortical bone (Figure 1). The expansile nature of these lesions may induce pressure atrophy of the surrounding bone, with loss of bony trabeculae or cortical bone and replacement by connective tissue (Figure 2). Bone cysts may be unilocular (Figure 3) or multilocular and may contain variable amounts of erythrocytes, fibrin, or proteinic material (Figure 4). Solitary bone cysts are rarely observed in the F344 rat, and their significance and pathogenesis are not known. These lesions may occur anywhere along the diaphysis; however, cysts may occur within the subchondral bone as a component of joint degeneration or osteochondrosis in the rat.
Leininger JR, Riley MGI. 1990. Bones, joints, and synovia. In: Pathology of the Fischer Rat: Reference and Atlas (Boorman G, Eustis SL, Elwell MR, Montgomery CA, MacKenzie WF, eds). Academic Press, San Diego, 209-226.
Long PH, Leininger JR. 1999. Bones, joints, and synovia. In: Pathology of the Mouse (Maronpot R, Boorman G, Gaul BW, eds). Cache River Press, St Louis, 645-678.
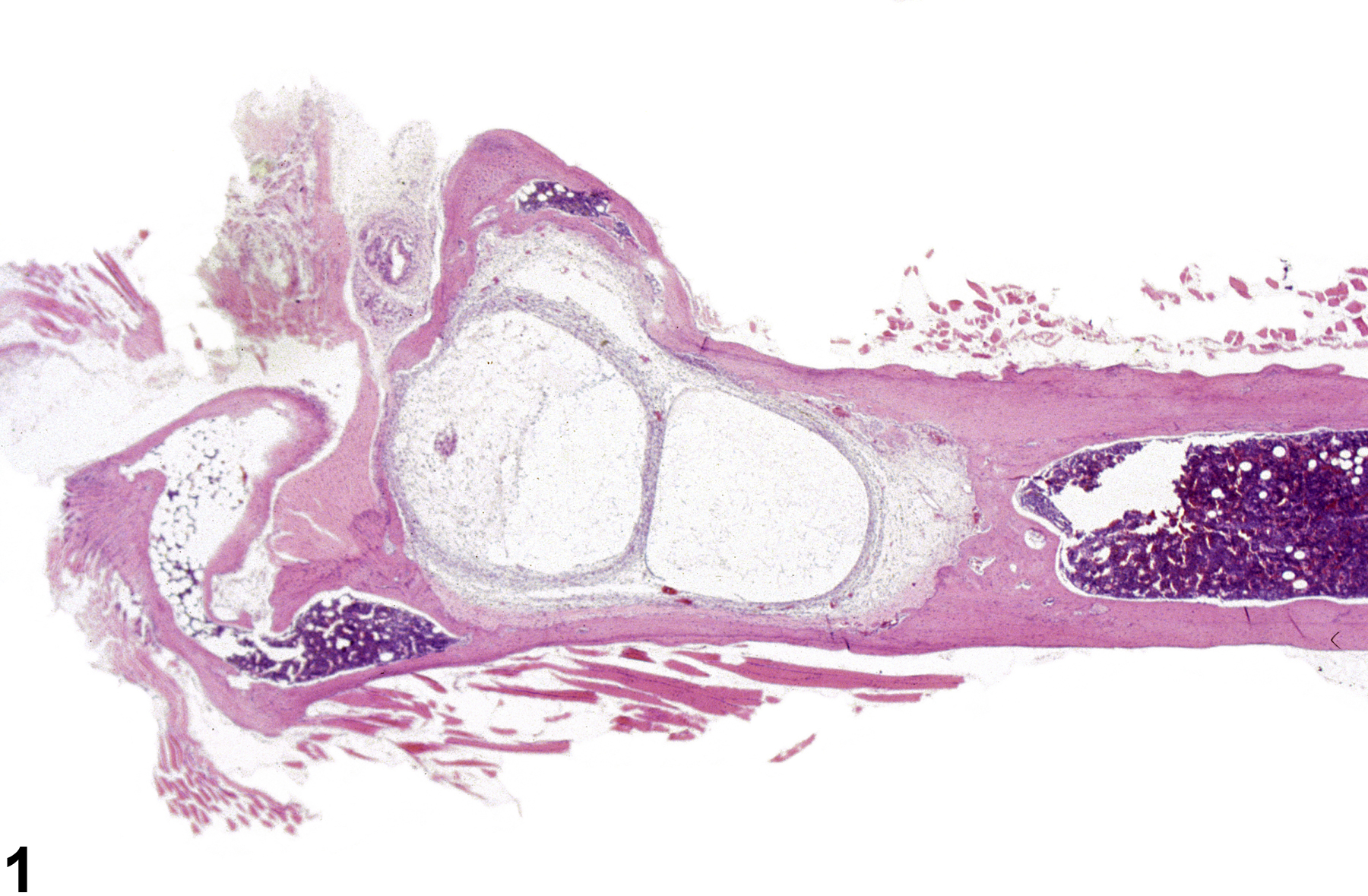
Bone - Cyst in a female B6C3F1/N mouse from a chronic study. The cyst is expansile and has a thin wall of cortical bone.





