Hematopoietic System
Bone Marrow - Pigment
Narrative
Increased hemosiderin of the bone marrow is associated with old or chronic hemorrhage or hemolytic anemia or is due to the administration of excessive amounts of oral or parenteral iron (iron overload). Anemia of inflammatory (or chronic) disease may also result in increased bone marrow hemosiderin. This is due to increased production of hepcidin, a key mediator of anemia of inflammation, by the liver. Hepcidin plays a role in maintaining normal iron homeostasis by inhibiting absorption of dietary iron from the intestinal epithelium and preventing the export of iron from macrophages. Inflammatory and neoplastic disorders cause an increase in hepcidin production that with time results in increased iron stores within the bone marrow. These iron stores are unavailable for erythropoiesis, subsequently contributing to the development of anemia.
While golden brown pigment within the bone marrow is presumed to be hemosiderin, it cannot be confirmed without special stains. Thus, “pigment” is deemed the most appropriate diagnosis. Increases in pigment in subchronic and chronic studies should always be documented, with grading based on the relative amounts of pigment present in comparison with same-site concurrent controls. When an increase in pigment is treatment related, it should be described in the narrative as being consistent with hemosiderin.
Braumann A, Wulfhekel U, Düllmann J, Nielsen P. 1992. Iron overload of the bone marrow by trimethylhexanoyl-ferrocene in rats. Acta Anat 144:285-295.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1414192Harvey JW. 2008. Iron metabolism and its disorders. In: Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals (Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML, eds). Elsevier, Burlington, MA, 259-285.
Abstract: http://www.elsevier.com/books/clinical-biochemistry-of-domestic-animals/kaneko/…Hejtmancik MR, Treka BA, Kurtz PJ, Persing RL, Ryan MJ, Yarrington JT, Chhabra RS. 2002. Comparative gavage subchronic toxicity studies of o-chloroaniline and m-chloroaniline in F344 rats and B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Sci 69:234-243.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12215679Nemeth E, Rivera S, Gabayan V, Keller C, Taudork S, Pedersen BK, Ganz T. 2004. IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of inflammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J Clin Invest 113:1271-1276.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15124018Nemeth E, Tuttle MS, Powelson J, Vaughn MB, Donovan A, Ward DM, Ganzand T, Kaplan J. 2004. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 306:2090-2093.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15514116Travlos GS. 2006. Histopathology of the bone marrow. Toxicol Pathol 34:566-598.
Abstract: http://tpx.sagepub.com/content/34/5/566.abstractTravlos GS, Mahler J, Ragan HA, Chou BJ, Bucher JR. 1996. Thirteen-week inhalation toxicity of 2- and 4-chloronitrobenzene in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 30:75-92.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8812232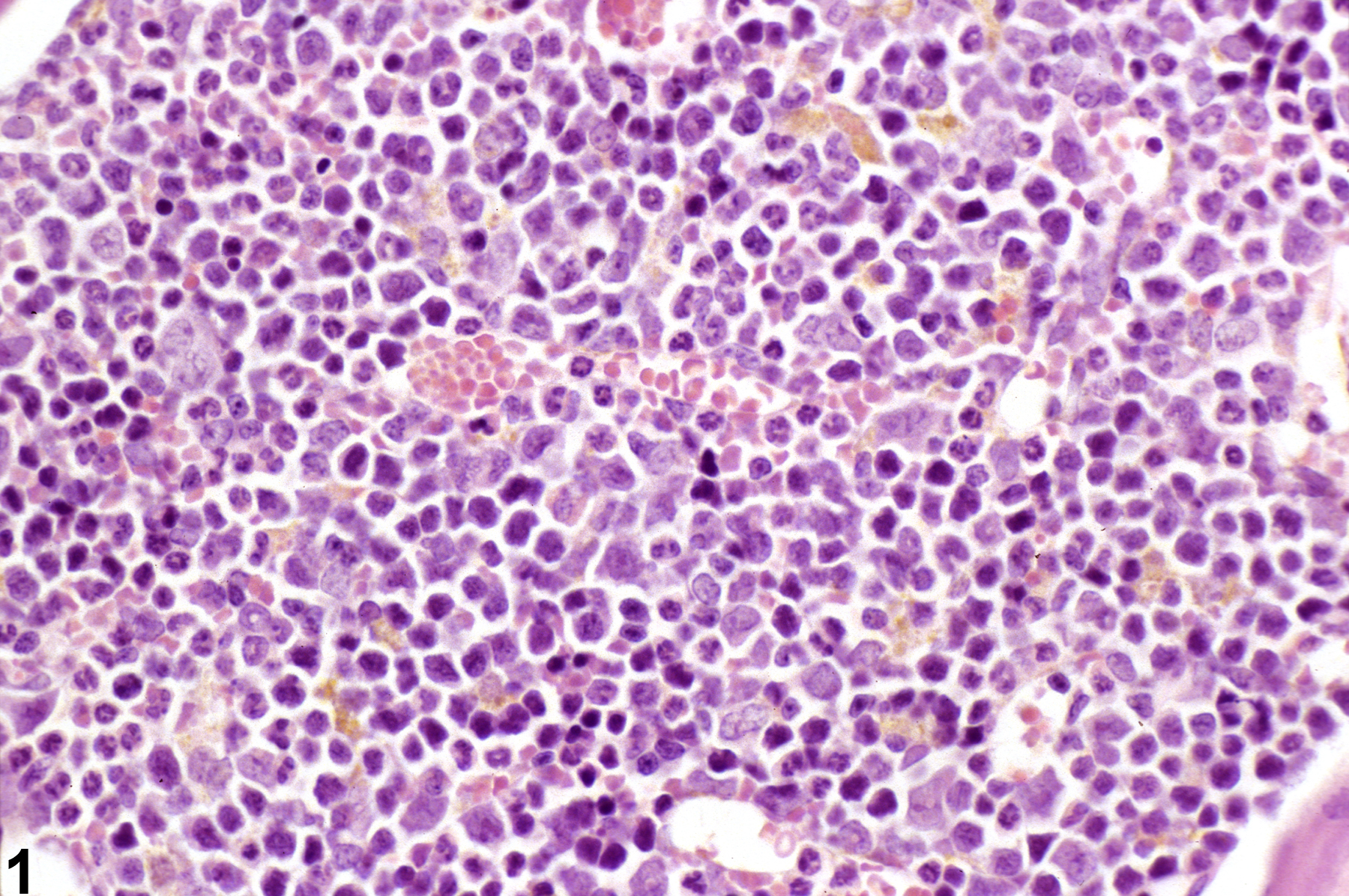
Low amounts of golden brown pigment in bone marrow in a male B6C3F1 mouse from a subchronic study.



