Musculoskeletal System
Bone - Physeal Dysplasia
Narrative
Physeal dysplasia may occur as a result of disturbances in mineralization secondary to nutritional deficiencies, metabolic disease, or chemical exposure. When these lesions occur as a result of a nutritional disturbance (deficiency in vitamin D, calcium, or phosphorus) in mineralization, particularly at the growth plate, they are referred to as rickets. Often, the term "osteomalacia" has been used to describe defective mineralization of epiphyseal cartilage; however, this is not the preferred nomenclature, since "osteomalacia" (see ) is used to describe increased amounts of unmineralized bone matrix (osteoid) causing generalized thickening of bony trabeculae, and an overall decrease in bone density, rather than delayed or impaired mineralization of physeal or epiphyseal cartilage, as seen in physeal dysplasia. Furthermore, the term "osteomalacia" denotes a gross morphologic change and should be considered inappropriate for histologic characterization. Compounds interfering with calcium, phosphorus, or vitamin D metabolism may result in disturbances in mineralization. Dysplasia of cartilage may also result from defective mineralization induced by chemical exposure or metabolic disturbances.
Dittmer KE, Thompson KG. 2011. Vitamin D metabolism and rickets in domestic animals: A review. Vet Pathol 48:389-407.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20634407Frazier K, Thomas R, Scicchitano M, Mirabile R, Boyce R, Zimmerman D, Grygielko E, Nold J, DeGouville A, Huet S, Laping N, Gellibert F. 1997. Inhibition of ALK5 signaling induces physeal dysplasia in rats. Toxicol Pathol 35:284-295.
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17366323Leininger JR, Riley MGI. 1990. Bones, joints, and synovia. In: Pathology of the Fischer Rat: Reference and Atlas (Boorman G, Eustis SL, Elwell MR, Montgomery CA, MacKenzie WF, eds). Academic Press, San Diego, 209-226.
Long PH, Leininger JR. 1999. Bones, joints, and synovia. In: Pathology of the Mouse (Maronpot R, Boorman G, Gaul BW, eds). Cache River Press, St Louis, 645-678.
Long PH, Leininger JR, Ernst H. 1996. Proliferative lesions of bone, cartilage, tooth, and synovium in rats, MST-2. In: Guides for Toxicologic Pathology. STP/ARP/AFIP, Washington, DC.
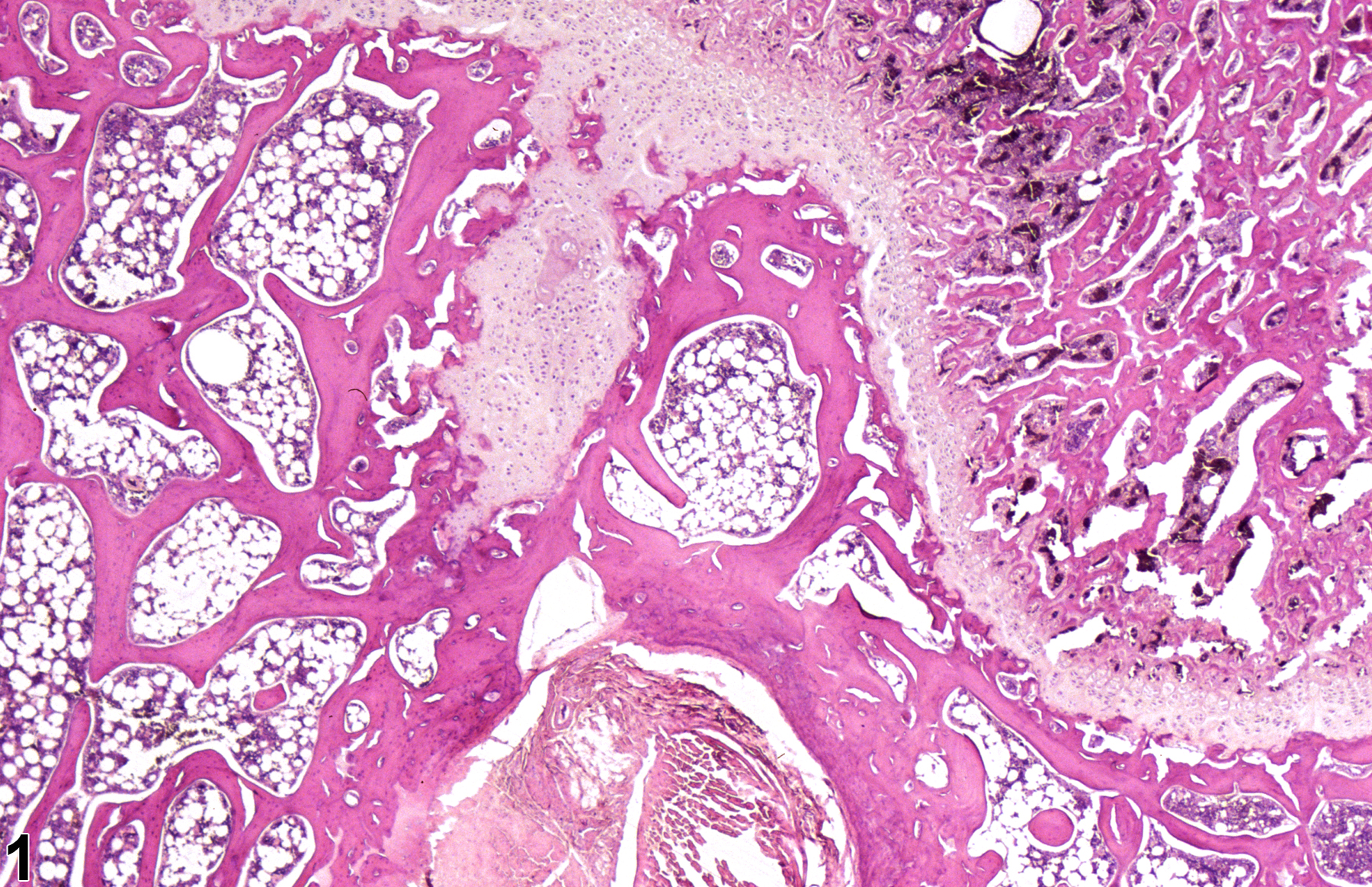
Bone - Physeal dysplasia in a male F344/N rat from a subchronic study. The cartilaginous growth plate is thickened and disorganized.




